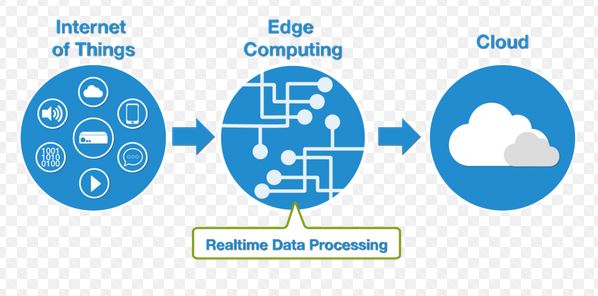
Sometimes, cloud computing and edge computing are discussed as mutually exclusive approaches to network infrastructure. Utilizing one does not preclude the use of other, they may function in different ways. They actually complement one another in practice quite effectively.
What is Cloud Computing?
All data is gathered and processed in a centralized location in a cloud computing architecture. Usually, this data lies in a data center. All devices must connect to the cloud if they need to use the application that is associated with the cloud. If devices are in need of data, they can’t get it without access on the cloud. Cloud is easy to control and secure while still allowing for reliable remote access because everything is centralized.
Who are Cloud Providers?
Amazon, Microsoft, and Google are providing public cloud services such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. These tech giants are also providing study material and taking exams for their certifications. For instance, Microsoft is giving certification to them who pass their cloud exam of Microsoft Azure Administrator AZ-103. With proper AZ-103 preparation, an individual can get this certification and brighten his/her career.
Is Cloud Secure?
Only authorized users can access tools and information form the cloud. This makes the cloud more secure and reliable. An organization can store information and assets in a centralized cloud and users can access it anytime from anywhere.
Data gathered from the edge of the network is difficult to process quickly and effectively due to the centralized nature of cloud computing. Cloud lacks speed but it makes up in capacity and power. Cloud can expand its processing capacity and storage as needed because cloud computing is based upon a scalable data center infrastructure. For small businesses that are looking to expand quickly, this scalability is a huge benefit for them.
Limitation of Edge Devices:
Any kind of big data for analytics can’t be processed by edge devices because edge devices only accumulate locally collected data. This makes it difficult for edge devices. Things that are not possible at the edge of the network like analysis of big data, cloud computing is capable of doing them.
Cloud can gather massive amounts of data with its processing potential and unparalleled storage. To produce valuable solutions, trends, and insights in a variety of ways the cloud can gather massive amounts of data. Machine Learning and artificial intelligence are now more viable with the data analysis capabilities of cloud computing.
For Datacenter infrastructures, cloud computing is a valuable source. In the tech industry, IoT devices represent an exciting new frontier, by moving assets to the edge of the network, not all businesses will see much benefit. For instance, many service providers for the cloud can provide better security and other services by hosting their products in a centralized cloud.
What is Edge Computing?
A vast amount of data is being generated on the outer “edge” of the computing networks as the internet of things devices incorporate more processing power and become more common. The data is produced by IoT devices. Usually, this data (that is created by IoT devices) is relayed back to a central network server. These servers are housed in a data center. Further instructions are sent back to the devices out on the edge of the network, once the data is processed.
But this setup has two problems:
1- Time to Travel
2- Strain on Bandwidth
Time to Travel:
The first is time to travel. To travel from the edge of the network to the center for processing, it takes time. Some times it is just a delay of milliseconds. Sometimes it can be critical. Even if the delay is of milliseconds it is still meant huge while processing.
The Strain on Bandwidth:
Secondly, between the center of the network and edge, all the data that is traveling back and forth puts tremendous strain on bandwidth. The combination of high volume and distance can slow the network down to crawl or network can even get crashed.
For IoT devices, Network latency can have serious sequences. For instance, consider self-driving cars. From other devices and their surroundings, autonomous vehicles gather a tremendous amount of data. Now think for the slightest delay of response. It could literally be a matter of life and death. If you’re unfamiliar with how network latency works, you can check out this helpful article to define latency.
Ending Thoughts:
Choosing cloud or edge computing isn’t an “either/or” proposition, fortunately. Organizations will need to implement effective edge computing architectures as the Internet of Things (IoT) devices become more powerful and widespread. By implementing these architectures properly, organizations can leverage the potential of this technology.
While minimizing their limitations, companies can maximize the potential of both approaches by incorporating centralized cloud computing (fog computing) with edge computing. This can be done by colocating IT infrastructure with a data center.